The Automotive Electronics Council (AEC) Standards

The Automotive Electronics Council (AEC) is an organization with purpose of establishing common part-qualification and quality-system standards. The AEC Component Technical Committee is the standardization body for establishing Standards for Reliable, High Quality Electronic components.

AEC documents are designed to serve the automotive electronics industry through eliminating misunderstandings between manufacturers and purchasers, facilitating interchangeability and improvement of products, and assisting the purchaser in selecting and obtaining with minimum delay the proper product for use by those other than AEC members, whether the standard is to be used either domestically or internationally.
Components meeting these specifications are suitable for use in the harsh automotive environment without additional component-level qualification testing.
The technical documents developed by the AEC Component Technical Committee are available at the AEC web site.
Most commonly referenced AEC documents are:
- AEC – Q100: Failure Mechanism Based Stress Test Qualification For Integrated Circuits
This document contains a set of failure mechanism based stress tests and defines the minimum stress test driven qualification requirements and references test conditions for qualification of Integrated circuits (ICs). These tests are capable of stimulating and precipitating semiconductor device and package failures.
The objective is to precipitate failures in an accelerated manner compared to use conditions. This set of tests should not be used indiscriminately.
- AEC – Q101: Failure Mechanism Based Stress Test Qualification For Discrete Semiconductors
This document defines minimum stress test driven qualification requirements and references test conditions for qualification of discrete semiconductors (e.g. transistors, diodes, etc.). This document does not relieve the supplier of their responsibility to meet their own company’s internal qualification program.
In this document, “user” is defined as any company developing or using a discrete semiconductor part in production. The user is responsible to confirm and validate all qualification and assessment data that substantiates conformance to this document.
- AEC – Q102: Failure Mechanism Based Stress Test Qualification for Discrete Optoelectronic Semiconductors
This document defines the minimum stress test driven qualification requirements and references test conditions for qualification of optoelectronic semiconductors (e.g., light emitting diodes, photodiodes, laser components) in all exterior and interior automotive applications.
It combines state of the art qualification testing, documented in various documents (e.g., JEDEC, IEC, MIL-STD) and manufacturer qualification standards.
- AEC – Q103: Failure Mechanism Based Stress Test Qualification for Sensors
This document contains a set of failure mechanism based stress tests specific to Micro ElectroMechanical Systems (MEMS) Microphone technologies used in vehicle cabin environments. This document shall be used in conjunction with AEC-Q100.
The circuit elements of MEMS devices are susceptible to the same mechanisms as standard IC’s, thus must meet the requirements defined in AEC-Q100.
- AEC – Q104: Failure Mechanism Based Stress Test Qualification For Multichip Modules (MCM)
This document contains a set of failure mechanism based stress tests and defines the minimum stress test driven qualification requirements and references test conditions for qualification of multichip modules (MCM). A single MCM consists of multiple electronic components enclosed in a single package that perform an electronic function.
- AEC – Q200: Stress Test Qualification For Passive Components
This specification defines the minimum stress test driven qualification requirements and references test conditions for qualification of passive electrical devices. This document does not relieve the supplier of their responsibility to meet their own company’s internal qualification program or meeting any additional requirements needed by their customers. In this document, “user” is defined as all companies that adhere to this document. The user is responsible to
confirm and validate all qualification and assessment data that substantiates conformance to this document.
Stress-Test “Qualification” is defined as successful completion of test requirements outlined in this document. The minimum temperature range required for each passive electrical component type is listed below (maximum capability) as well as example applications typical of each grade (application specific):
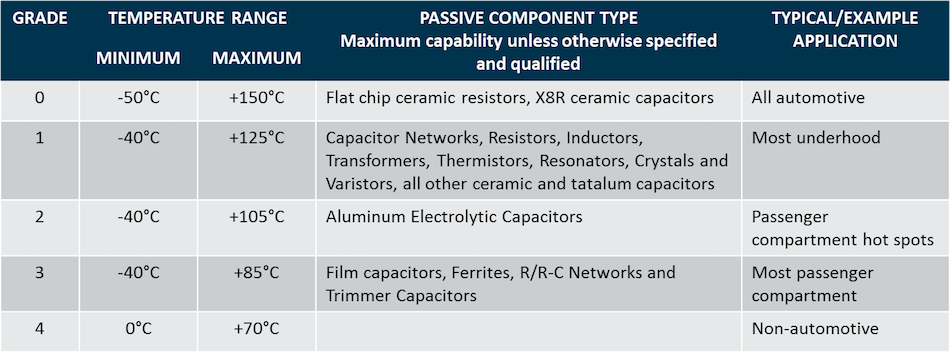
Qualification of the noted device type to its minimum temperature grade allows the supplier to claim the part as “AEC qualified” to that grade and all lesser grades. Qualification to temperatures less than the minimum specified above would allow the supplier to claim the part as “AEC qualified” at the lower grade only.
Determining the temperature grade of a passive component type or an application not mentioned above should be agreed to between the supplier and user.
AEC documents are adopted without regard to whether or not their adoption may involve patents or articles, materials, or processes. By such action AEC does not assume any liability to any patent owner, nor does it assume any obligation whatever to parties adopting the AEC documents. The information included in AEC documents represents a sound approach to product specification and application, principally from the automotive electronics system manufacturer viewpoint. No claims to be in Conformance with these documents shall be made unless all requirements stated in the document are met.
Read More : AEC (Automotive Electronics Council)
MICROREL offers Consulting Services in Partnerships with external Certified Laboratories specialized in High-Reliability EEE Parts Procurement services for the Electronic Components and RF Microwave parts to the Military Standards requirements from Program Management to Parts Engineering for Military and Aerospace application requirements.









