Electronic Parts Inventory Excess impact Warehousing costs

If you are involved in EMS manufacturing Industry, you can end up with excess inventory for many reasons:
- Program schedule imposes Advanced procurements although production department BOM (Bill of Material) not yet frozen or wrong estimation of how many finished products could have been actually sell to market.
- Obsolescence and/or End of Life issues could require building strategic stock to be able to manufacture Equipment’s over a period longer than the Product life cycle
- Electronic Manufacturing Systems (EMS) across the World highlight shortage of Semiconductors, Microchips or Electronic components in general and activate Strategic Advance Procurements at risk.
-
Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ) often imposed by Suppliers become aftermarket service parts inventory issue.
-
Inventory optimization also relies on accurate Lead Times for all processes that are part of replenishment cycle however, in practice, most businesses don’t have a means of measuring these accurately.
-
Design Engineering targets to improve their products performances of Equipment manufactured with this parts are constantly changing with result of replacement specific anc costly Material Parts previously procured and in Store.
Hence Forecast parts demand is much more complex than planning demand for a manufacturing operation.
Result is that Store production overruns in inventory will increase Overall warehousing costs due to Excessive Ordering.
Excess inventory cost impact
Carrying costs are costs associated with storing inventory in your warehouse and are made up of these different elements:
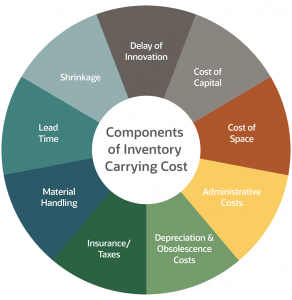
- Capital costs: Includes everything related to your investment in buying the stock, e.g the cost of the stock, the interest on working capital and the opportunity cost.
Opportunity costs are the difference between investing in stock or investing in other business activities. For example, if most of your cash is tied up in inventory, you lose the opportunity to invest in other areas of the business, such as marketing activity, new machinery, or taking on more employees. - Storage space costs: a combination of the warehouse rent or mortgage and maintenance costs, such as lighting, heating and air conditioning.
- Service costs: include insurance, security, IT hardware and the cost of physically handling the goods.
- Inventory risk costs: the risk that items might fall in value over the period they are stored, shrinkage and the risk that they become obsolete.
Excess inventory can lead to poor Quality and degradation
Excess stock that sits on warehouse shelves can begin to deteriorate and perish. So, businesses often sell off perishable or sub-standard stock at lower prices to prevent having to throw it away and lose its value altogether. Discounting stock or disposing of it altogether can have a significant impact on your business’s profitability.
Several Solutions for parts inventory management are available for a variety of manufacturing sectors including Automotive, Aerospace and Defense sectors for which the Cost of Electronic Parts impacts overall Warehousing costs.
For instance the European ESCC standard ECSS-Q-ST-60-14C specifies the requirements, also known as “relifing requirements”, for the planned, intentional storage, control, and removal from storage of electronic, electrical and electromechanical parts which are intended to be used for space applications.
The relifing process is a Lot Quality Control (QC) activity and consists in the evaluation of the Electronic component Reliability when stored for a longer period. Storage of EEE part in fact represents a key process in the Space electronics.
The relifing process is aimed at detecting any degradation in the product performance that could affect the system performance for a long-term application summarized as follows:
- External visual inspection: to detect signs of corrosion, degradation of the sealing material or other potential defects
- Electrical measurements: to estimate the presence or absence of wear out caused by storage.
- Seal test: to verify the hermeticity of the components
- Solderability and Bondability test: to further verify any technological degradation of the components.
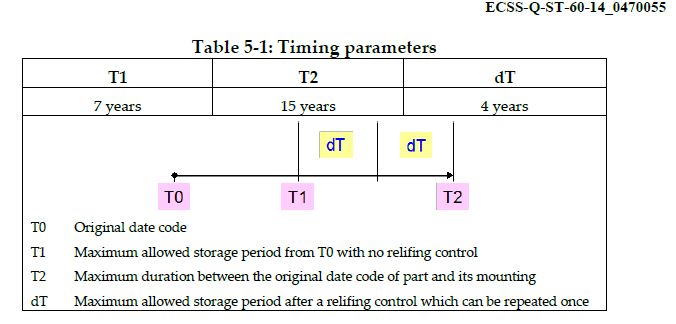
Timing parameters are the following :
If you have excess stock, you need to act fast to prevent it becoming obsolete.
Hence, aftermarket business needs a high degree of integration between the engineering and aftermarket service parts management areas of your business to avoid technical obsolescence.









